Production Process
Chemical Vapor Deposition
Conformity over complex 3D surfaces – Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a thin film deposition technology that provides uniform, dense, high-purity coatings with excellent step coverage and conformity over complex 3D surfaces. CVD reaction parameters allow for control of the coating composition, crystallinity, defect density, and internal stresses.
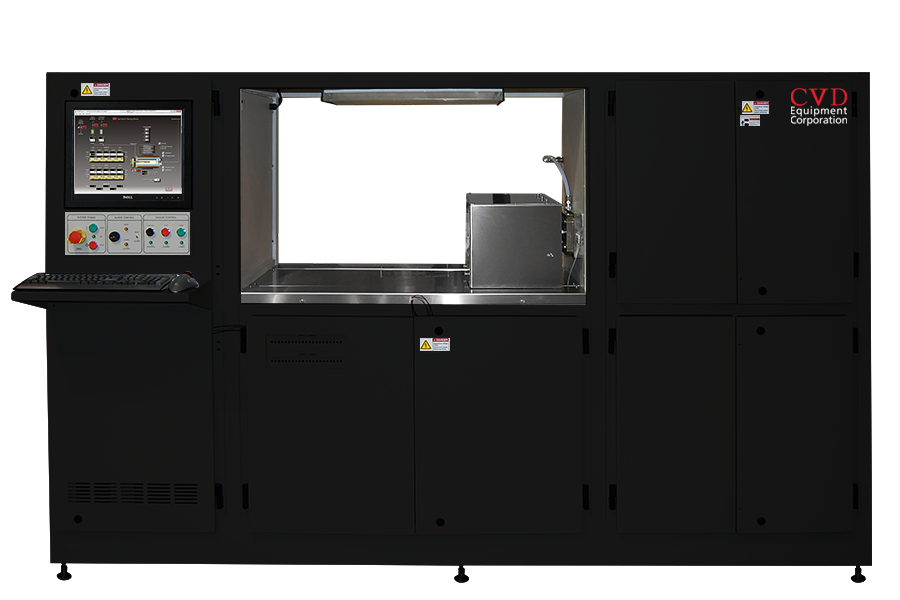
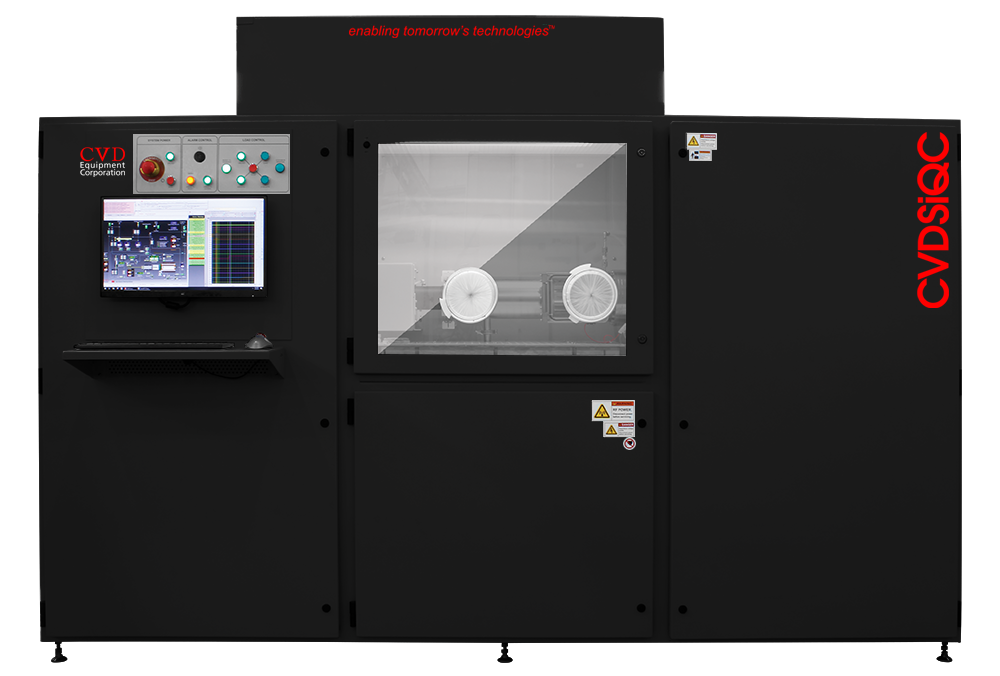
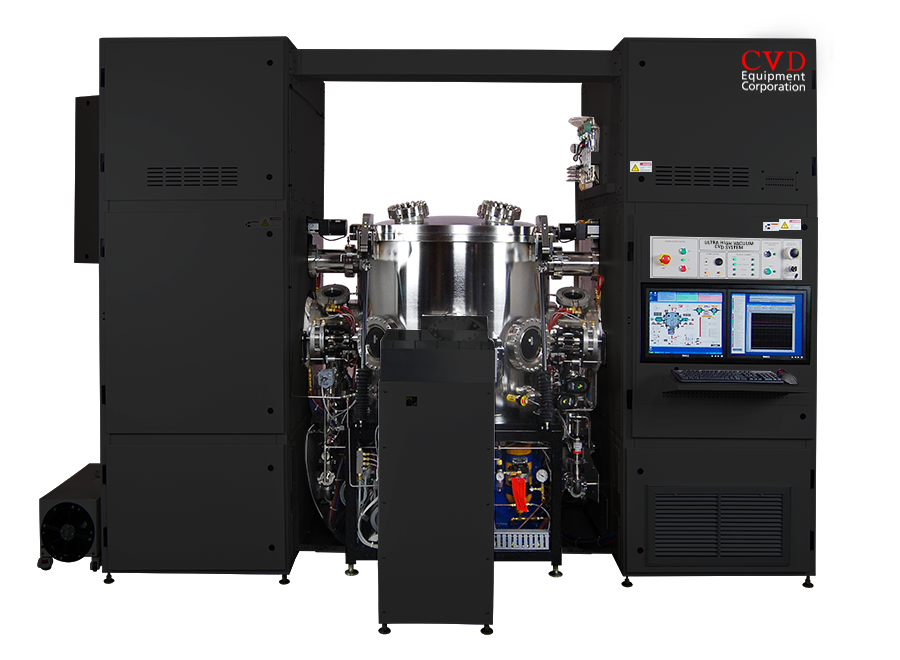
CVD Equipment Coating Systems
PVT Systems

HVPE Systems

LPE Systems

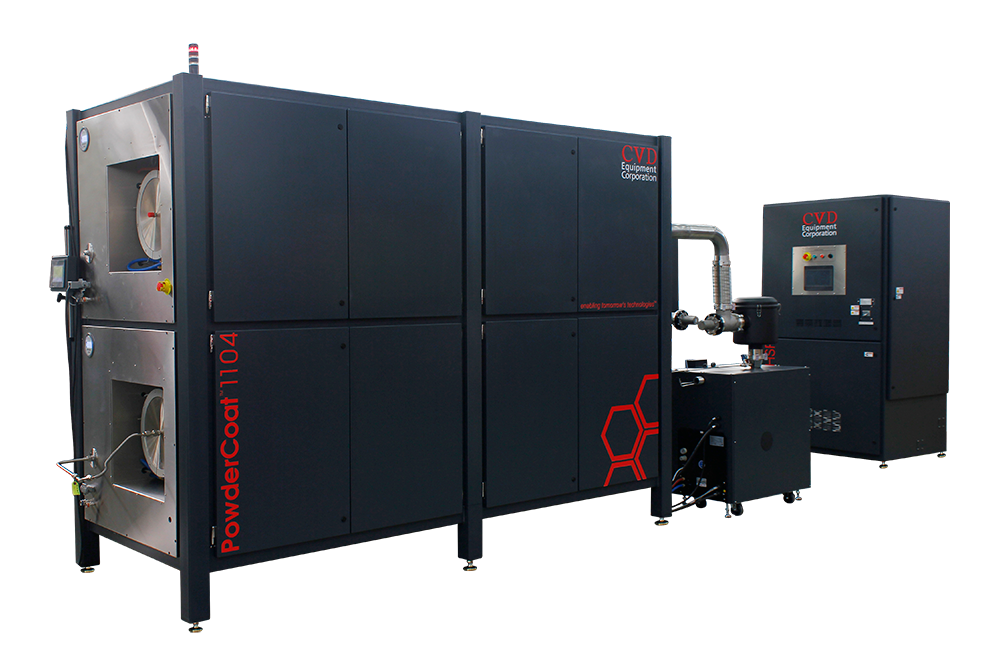
Powder Coat Systems

Fiber Coating Systems

CVI Systems

BondCoat™ Systems

Reel-to-Reel

Cluster Tools
MOCVD Systems

PECVD Systems

Speciality Systems
PROPERTIES & CHARACTERISTICS
Coatings Deposited by Chemical Vapor Deposition Enhance a Component’s Properties and Characteristics
Corrosion protection and barrier layers
Environmental coatings
Antifouling
Encapsulation
Friction/tribology
Wear resistance
Aesthetics/cosmetics
Hydrophobicity/hydrophilicity
Thermal conductivity/insulation
Electrical conductivity/insulation
Catalytic activity
Photon reflectivity/absorbance
Shock absorption
Compressibility
Mechanical bonding/interlocking
Surface or contact area
Fire retardancy
Biocompatibility
Coatings are often designed to perform multiple functions.
TYPES OF INDUSTRIAL COATINGS
OPTICAL PROPERTIES
Photoluminescent Coatings
Antireflective Coatings
Photochromatic Coatings
ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES
Antistatic Coatings
Conductive Coatings
Dielectric Coatings
THERMAL PROPERTIES
Heat Resistant Coatings
Thermal interface Coatings
Intumescent Coatings
STRUCTURAL PROPERTIES
Hard Coatings
Anti-Abrasion Coatings
Anti-Corrosion Coatings
BIOENGINEERED PROPERTIES
Anti-Microbial Coatings
Biocompatible Coatings
Bone Compatible Coatings
PHYSICO-CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
Photocatalytic coatings
Hydrophilic coatings
Hydrophobic Coatings
About Us
Over 40 years of expertise in CVD and thermal process equipment design and manufacturing.
“enabling tomorrow’s technologies ™ ”




